The concept that everything ingenious is simple and has already been invented before us holds true. This principle is also applicable to the innovative Pascal Machine AI project. The creators of this project have taken inspiration from the renowned French mathematician Blaise Pascal and applied his theories to modern tasks, harnessing the immense computational power of today’s computers. As a result, they have developed a sophisticated tool that enables them to make highly accurate mathematical predictions.
By utilizing this tool to forecast the movement of stock index quotations, the Pascal Machine AI project is able to generate forecasts with a high level of probability. This, in turn, enables them to execute a significant number of successful transactions, surpassing the number of unsuccessful ones. Ultimately, the project aims to generate substantial profits for its investors.

Now, let’s delve deeper into how this remarkable project operates.
What is the Connection to Blaise Pascal?
Blaise Pascal, a renowned figure in religious philosophy, writing, mathematics, and physics, serves as the inspiration behind the Pascal Machine AI project.
At the young age of 19, Pascal embarked on the development of his own calculating device. This invention is considered to be one of the early versions of the calculator. Growing up with a tax collector for a father, Pascal had firsthand exposure to various mathematical operations. It was during this period that he sketched out the initial designs for his creation, known as the Pascaline. The entire process of perfecting the device took a total of five years.
In theory, Pascal’s mechanism was relatively straightforward to operate. However, due to limited technological advancements, bringing the scientist’s vision to life proved to be a challenging task that required overcoming numerous difficulties. Blaise’s goal was to create a machine that could simplify complex calculations, catering to both highly skilled mathematicians and individuals with minimal arithmetic knowledge. Over a span of 10 years, Pascal developed more than 50 calculating machines, but only a few of his inventions were successfully sold.
What Is Blaise Pascal’s Machine?
Blaise Pascal’s Calculating Machine, also known as the Pascaline, is a compact apparatus comprised of multiple interconnected cogwheels or gears. Each wheel is intricately labeled from zero to nine. To carry out addition, one must rotate the gears accordingly to select and align the desired numbers. The wheels continue to rotate until the correct digit is displayed. If the sum exceeds nine, the remaining balance prompts the gear to shift to the next digit, simultaneously advancing the adjacent wheel by one increment.
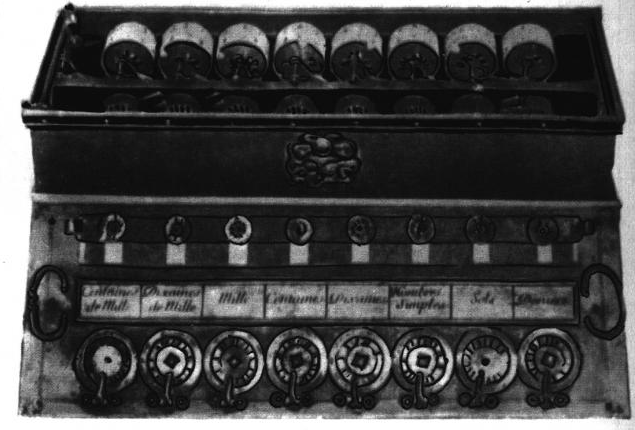

The utilization of wheel rotations for the process of addition was not an original concept in Pascal’s scientific endeavors, as this notion had been previously expressed by Wilhelm Schickard in 1623. In fact, Blaise’s invention is regarded as the incorporation of carrying over the remainder with a complete revolution of the gears. The initial “pascalines” featured five gear wheels, but as the technology progressed, the mechanism was modernized to include eight pieces, enabling the manipulation of larger numbers (up to 9999999). This mechanism found active application in various technical devices until the 20th century. Its notable advantage was the device’s ability to automatically add multi-digit numbers.
According to researchers studying the history of counting mechanisms, it is believed that Pascal developed his adding machine from scratch, without any knowledge of Schikkard’s project. This device amazed the scientific community of Pascal’s time, but its high cost and complexity made it difficult to gain popularity. Nonetheless, Pascal’s invention made a significant contribution to the evolution of computer technology.
At a specific point in Pascal’s life, he encountered a wealthy individual named the cavalier de Mere. The cavalier de Mere was an avid gambler who proposed a challenge to Pascal in 1654, asking him to solve certain problems that arise in specific gaming scenarios.
De Mere’s initial challenge, regarding the point at which the likelihood of winning surpasses the likelihood of losing after a certain number of dice throws, was successfully resolved by De Mere himself, as well as Pascal, Fermat, and Roberval. In their pursuit of solving the second, considerably more complex problem, which involved correspondence between Pascal and Fermat, the groundwork for the theory of probability was established. As scientists endeavored to address the issue of distributing bets among players in a series of interrupted games, they each applied their analytical methods for calculating probabilities and ultimately arrived at the same conclusion.
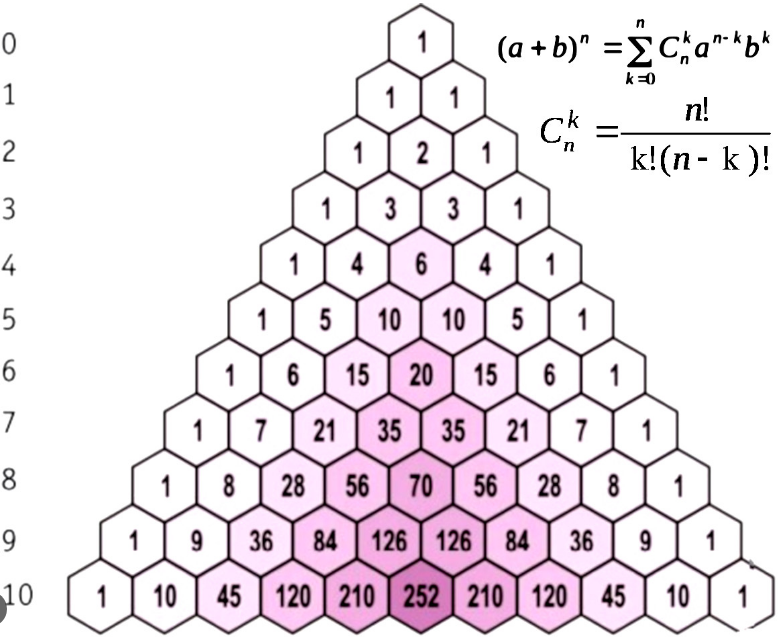
Pascal authored the “Treatise on Arithmetical Triangle” in 1665, where he delved into the characteristics of “Pascal’s triangle” and explored its utility in calculating combinations without relying on algebraic formulas.
Drawing inspiration from Pascal’s early works, the creators of Pascal Machine AI have developed their own project that is currently operational in today’s modern world.
Why hasn’t something like this been created earlier?
Pascal diligently performed his calculations on the triangle manually, during lengthy evenings. Contemporary computers have the capability to execute 10 to 12 operations per second. It is only by attaining such an immense computing power that the algorithms devised by Pascal three centuries ago can commence functioning and yield tangible outcomes for intricate processes.
The Market for Implementing Pascal’s Advancements
The stock market serves as a prime illustration of a sophisticated system, wherein numerous variables contribute to the ultimate outcome: the objectives of prominent investors and stakeholders, regional economic occurrences across various nations, political events, weather phenomena, and numerous other equally noteworthy factors. This provides an ideal platform for employing predictive algorithms. By considering hundreds of factors and analyzing vast amounts of data, Pascal Machine AI generates forecasts and precise recommendations derived from said forecasts. These recommendations are then utilized for genuine trading operations that yield tangible profits.
At present, the Pascal Machine AI is actively engaged in trading on the stock markets, focusing on stocks of successful startups that have demonstrated high growth potential. These startups hail from various countries, including Canada and Australia. Through its strategic buying and selling transactions, the Pascal Machine AI is able to generate substantial passive income.
How Does Pascal Machine AI Work?
Instead of delving into intricate algorithms used to calculate the Pascal triangle (which are readily available for study), let’s provide a concise explanation: Pascal Machine AI receives vast quantities of market data, which is then organized and broken down into thematic clusters. Next, Pascal’s algorithms are applied to these prepared clusters. Following the processing stage, the system generates an extensive list of factors, complete with assessments of their significance and likelihood of occurrence. These probabilities are carefully balanced, leading to the generation of a final decision. This decision serves as a trading signal, indicating whether to execute a transaction or hold onto specific securities.
Private investors now have the opportunity to capitalize on Pascal Machine AI, enabling them to engage in lucrative transactions with minimal investment. This groundbreaking technology opens doors for individuals to partake in profitable ventures, even with limited capital.
According to our perspective, the evolving nature of the AI market will ultimately result in the emergence of several rivals for the Pascal Machine AI initiative. As these projects operate within the same market, it is possible that there will be a decrease in the average returns for investors. However, at present, we have not observed any comparable projects that possess the ability to scale and progress like Pascal Machine AI does.
